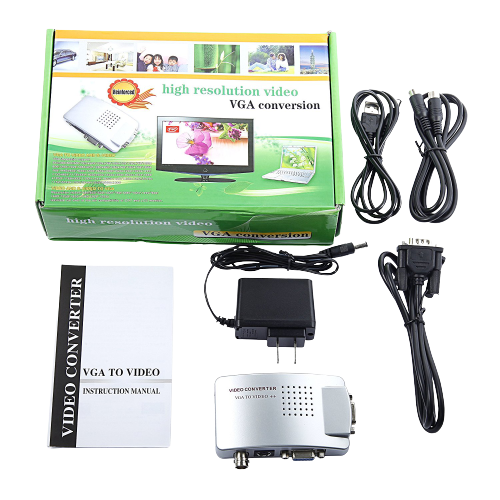
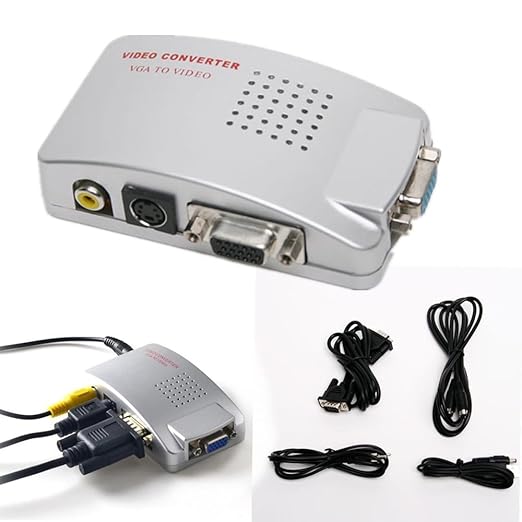
I. General Specifications for High-Resolution VGA Converters:
- Conversion Type:
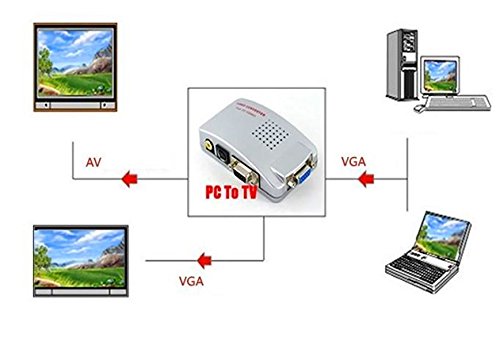
- VGA to Digital (most common for “high resolution”): Converts analog VGA to HDMI, DVI, or DisplayPort. These converters are directional (VGA in, digital out) and often require external power.
- VGA to Analog (less common for “high resolution” unless upscaling): Converts VGA to CVBS (composite video), S-Video, or component video. These might also upscale lower-resolution VGA signals.
- Bi-directional converters are rare and usually a combination of two separate converter functions.
- Supported Input Resolutions (VGA):
- Common PC resolutions: 640×480, 800×600, 1024×768, 1280×720, 1280×768, 1280×800, 1280×960, 1280×1024, 1360×768, 1366×768, 1440×900, 1600×900, 1600×1200, 1680×1050, 1920×1080, 1920×1200.
- Refresh rates often 60Hz, but some may support 70Hz, 75Hz, 85Hz.
- Supported Output Resolutions:
- For VGA to HDMI/DVI/DisplayPort:
- Standard: Up to 1080p (1920×1080) at 60Hz. This is the most common “high resolution” for these converters.
- PC Resolutions: Up to 1920×1200.
- Some specialized or higher-end converters might claim support for even higher resolutions like 2048×1536, but this becomes less common and depends heavily on the quality of the VGA source and cable.
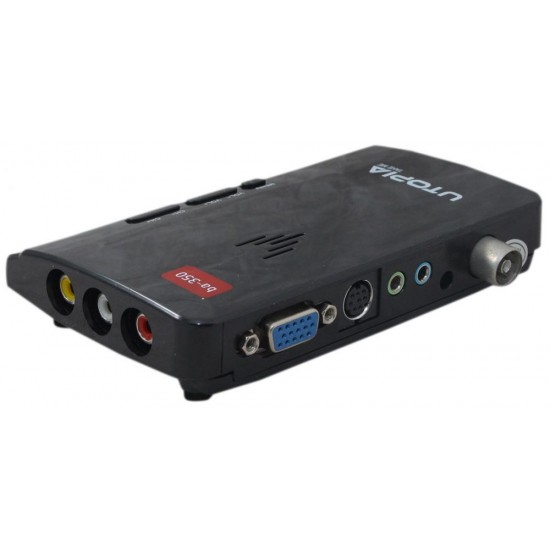
- For VGA to other analog formats (if applicable): Output resolutions typically match standard TV formats (e.g., 480i/p, 576i/p).
- For VGA to HDMI/DVI/DisplayPort:
- Audio Support:
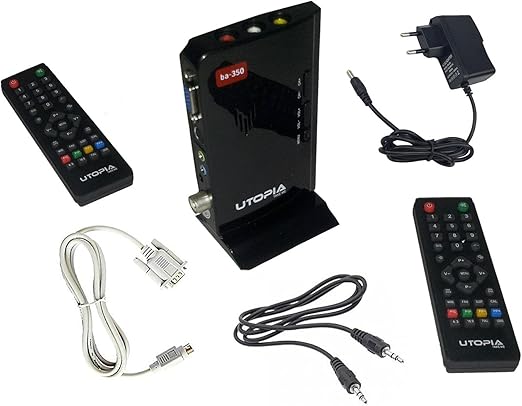
- Crucial for VGA to HDMI/DisplayPort converters: Since VGA is video-only, these converters usually have a 3.5mm audio input jack (or sometimes RCA stereo) to embed analog audio from the source into the digital output signal.
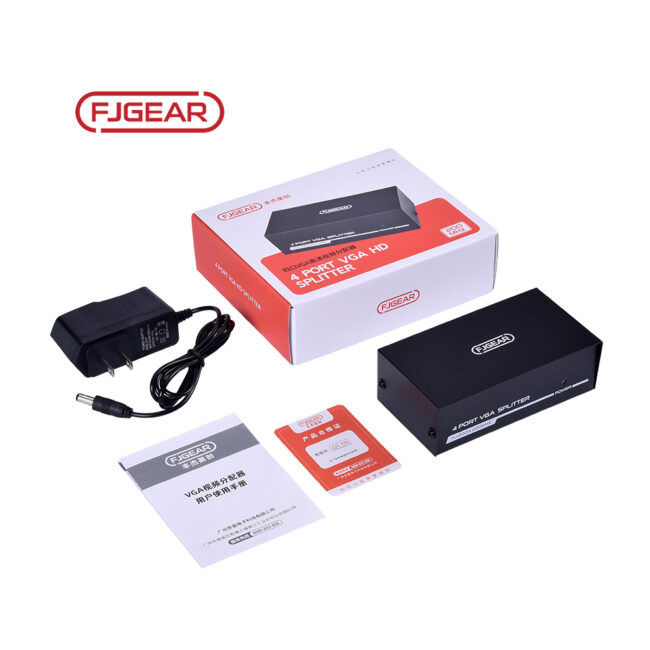
- Power Supply:
- Most high-resolution VGA converters require external power, often via a USB cable (Micro USB or USB-A) or a DC 5V power adapter. This is because they need to actively convert the analog signal to digital and scale it if necessary.













































 لا توجد منتجات في السلة.
لا توجد منتجات في السلة. 
المراجعات
لا توجد مراجعات حتى الآن.